When a critical service goes down, how long does it take your team to figure out why?
If the answer is longer than it should be, you face the same challenge as many modern IT teams.
IT Infrastructure is spread across on-premise systems, virtualized environments, cloud platforms, mobile devices, and containers. Assets are constantly added, reconfigured, or retired, often without clear documentation. In this environment, it’s alarmingly easy to lose track of what you have, where it’s running, who owns it, and how it connects to the services your business relies on.
According to IDC, 60% of organizations report that poor visibility into IT assets leads to higher risk and longer resolution times. This lack of centralized, trusted asset data makes incident response slower, change management riskier, compliance harder, and costs harder to control.
The ServiceNow Configuration Management Database ( CMDB ) is a single system of record for your entire IT infrastructure; it provides a clear, current, and connected view of your digital environment. It integrates directly with ServiceNow ITSM suite, helping IT teams respond faster, confidently manage changes, and reduce operational risk.
This blog will explore how organizations can overcome IT visibility challenges by utilizing ServiceNow CMDB to gain control over their digital infrastructure, streamline asset management, reduce operational risks, and make faster, more informed decisions.
Understanding CMDB: The Backbone of IT Service Management
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a centralized repository that stores detailed information about the components of an organization’s IT environment. In simple terms, a CMDB answers the following questions:
- What IT assets do we have?:
- Where are they located?:
- How are they connected or dependent on each other?:
- What is the status or health of each CI?:
- What changes have been made over time?:
- Who is responsible for managing or maintaining them?:
- How do incidents or problems affect related assets?:
| Function | Description |
|---|
| Inventory Management | Tracks what assets exist, their status, and where they are located. |
| Dependency Mapping | Maps how different components interact and depend on each other. |
| Change Impact Analysis | Assesses which services may be affected when a CI is modified or fails. |
| Problem Diagnosis | Identifies root causes of incidents by analyzing CI relationships. |
| Compliance and Audits | Maintain accurate records for asset tracking, regulatory audits, and reviews. |
The Role of CMDB in Delivering Reliable IT Services
Here is how the CMDB helps to streamline your IT infrastructure:
Incident Management
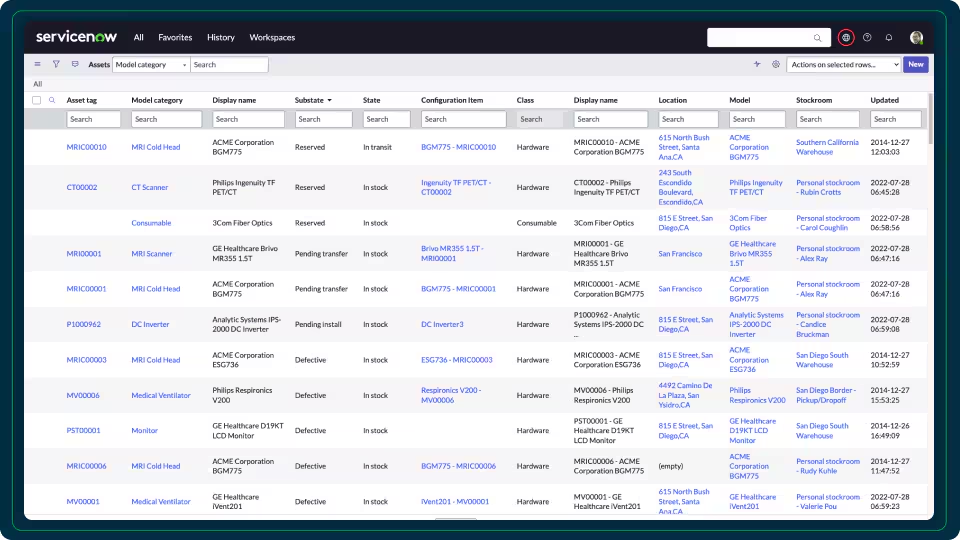
A CMDB helps IT staff quickly identify the affected Configuration Items (CIs) when a service disruption occurs. By understanding dependencies, teams can trace the issue to the root cause and respond faster. This leads to reduced downtime and quicker service restoration.
Problem Management
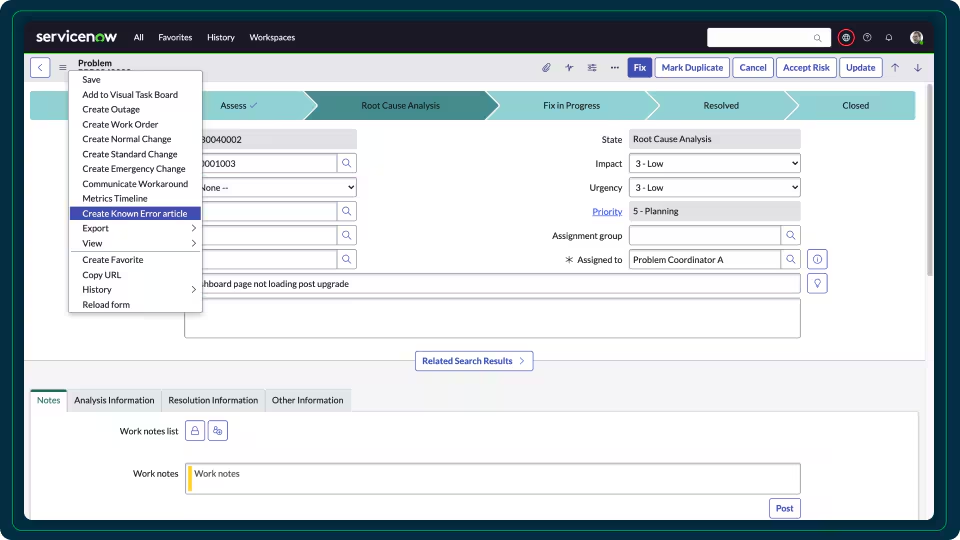
CMDB data helps identify recurring incidents linked to the same CI or group of CIs. It enables pattern recognition and root cause analysis across incidents, resulting in permanent fixes, not just temporary solutions.
Change Management
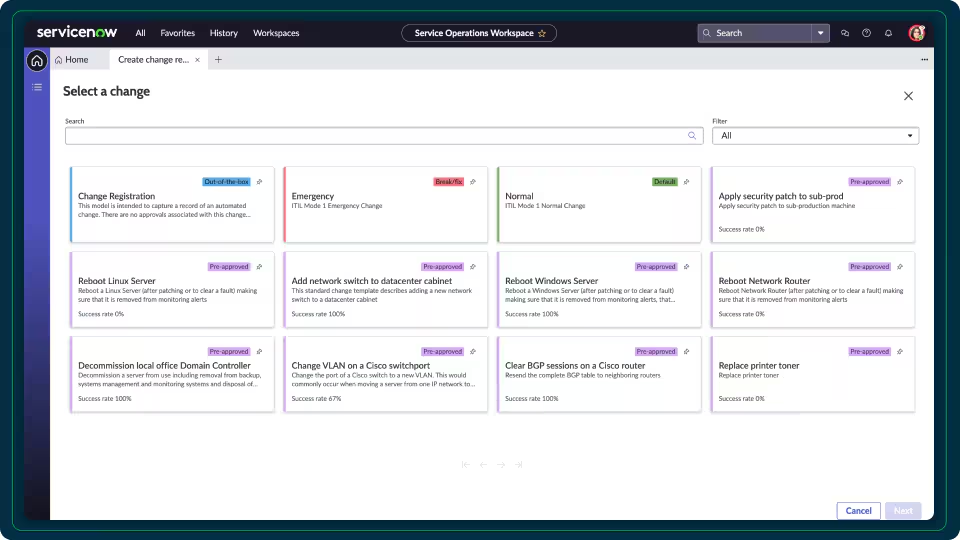
Before changing any system, it is critical to know what other systems or services may be impacted. The CMDB provides a map of relationships and dependencies, enabling better risk assessment. It also ensures that changes are planned, approved, and implemented with minimal disruption.
Components of a CMDB: Core Elements You Need to Know
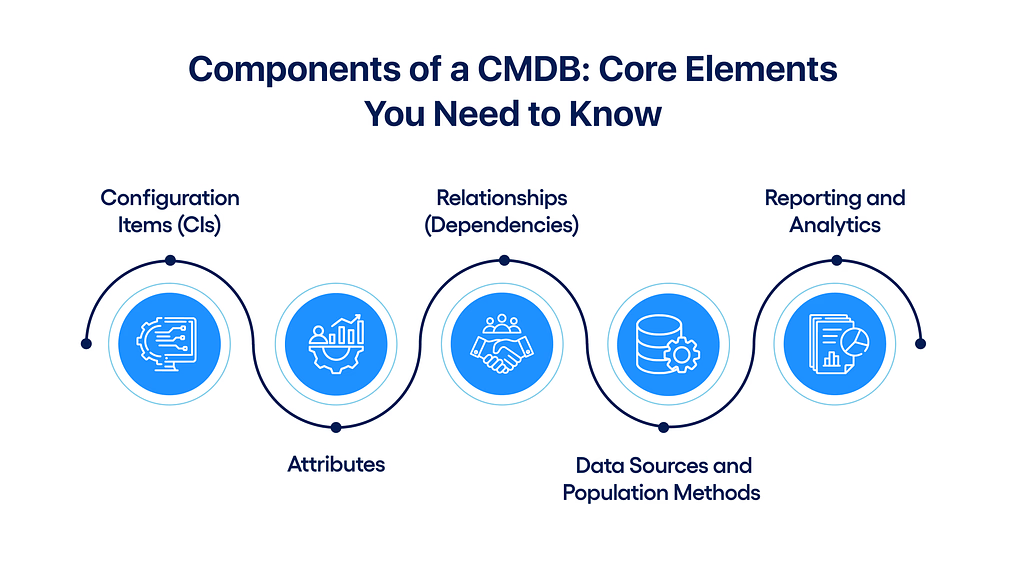
Below is a breakdown of each core component and its role within the CMDB structure in ServiceNow.
Configuration Items (CIs)
Configuration Items (CIs) are the core units tracked in a CMDB. A CI can be a physical asset like a laptop, a software application, or even a service such as payroll or email.
In ServiceNow, each CI is recorded with detailed information, like a profile, and grouped into logical categories for easy access.
- Hardware: Servers, routers, laptops, storage devices.
- Software: Applications, operating systems, middleware.
- Network components: Switches, firewalls, access points.
- Databases: SQL servers, NoSQL clusters.
- Cloud resources: Virtual machines, containers, load balancers.
- Business services: Email service, customer portals, HR systems.
- People and documents (less commonly): Users, process documentation, service level agreements (SLAs).
Attributes
Attributes are the descriptive fields linked to each CI. They provide granular details that help identify and manage the asset. Examples of CI attributes include name, IP address, owner or department, location (physical or virtual), version or firmware, maintenance schedule, and operational status (active, retired, under maintenance). Accurate attributes are critical for managing lifecycles, assessing impact, and ensuring compliance.
Relationships (Dependencies)
CMDBs also track how CIs are connected. These relationships define dependencies between components essential for troubleshooting and impact analysis. For example, a mobile app is integrated with a cloud-based identity provider for user authentication, or an application runs on a specific server.
ServiceNow displays these relationships visually through dependency maps, which help IT teams quickly assess the ripple effects of incidents, outages, or planned changes.
Data Sources and Population Methods
The CMDB must be regularly populated and updated to stay accurate and complete. ServiceNow provides multiple ways to gather data:
- Automated Discovery: Scans networks, devices, and services to detect CIs and auto-fill data.
- Service Mapping: Links CIs to the business services they support
- Integration Tools: Pull data from external systems like asset management tools or monitoring platforms.
- Manual Entry: This is used for low-volume or unique CIs.
- Import Sets: Bulk upload of CI data from files like spreadsheets.
Reporting and Analytics
An effective CMDB should allow IT teams to generate insights and reports based on the data it holds. ServiceNow includes built-in analytics tools that support CI health tracking, incident and change correlation, service impact analysis, compliance reporting, and lifecycle status dashboards. These tools help organizations make informed decisions, identify risks early, and improve operational efficiency.
How Does a CMDB Work?
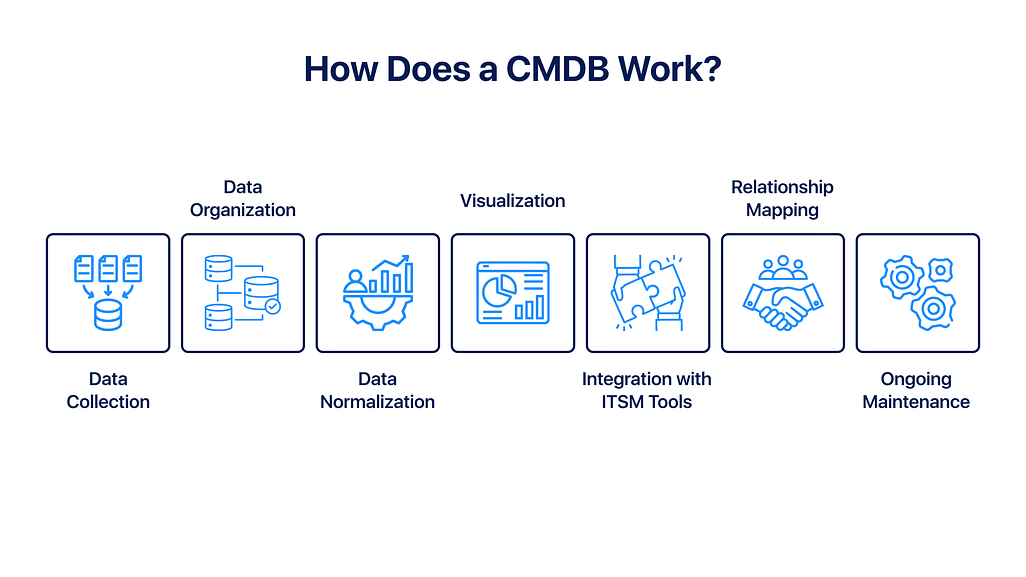
Here is an explanation of how a CMDB collects, organizes, and maintains configuration data to support IT operations.
Data Collection
The first step is gathering information about IT assets, called Configuration Items (CIs). These include physical devices, software, network components, and services.
Data can be collected in several ways. Automated discovery tools are commonly used to scan networks and systems, automatically detecting configuration items (CIs) and capturing details such as IP addresses, software versions, hardware specifications, and operational status.
Manual input may be appropriate for smaller environments or niche assets, allowing teams to enter information for specific components directly. Additionally, data can be imported from external sources, such as spreadsheets or other IT management tools, to quickly populate or update the CMDB without starting from scratch. A diverse set of sources ensures that the CMDB captures a complete and accurate view of the IT environment.
Data Organization
Once the data is collected, it must be sorted and structured to make it usable. Each CI is classified as hardware (e.g., servers, laptops), software (e.g., business applications), and network Equipment (e.g., switches, routers). Each CI is also assigned attributes such as name, version, location, and status. Organizing the data this way makes it easier for IT teams to manage, search, and analyze.
Data Normalization
Raw data often comes in different formats from various sources. Normalization standardizes this information to eliminate duplicates, align naming conventions, and ensure consistency.
For example, a server detected by two tools might appear under slightly different names. Normalization merges these entries and applies a uniform format. This step is essential for maintaining data quality and avoiding confusion during analysis or troubleshooting.
Visualization
Most modern CMDBs, including ServiceNow, offer visual tools to display CI relationships and dependencies. These diagrams, often shown as service maps, help IT professionals understand the structure of services, spot weak points or potential risks, and navigate the impact of outages or changes. Visualization turns complex data into understandable formats, making it easier to make informed decisions.
Integration with ITSM Tools
A CMDB doesn’t work in isolation. It connects with IT Service Management (ITSM) tools to provide real-time context across various functions. These integrations ensure that the CMDB data supports day-to-day operations and strategic planning.
Relationship Mapping
Another function of the CMDB is identifying how CIs relate. These relationships show dependencies, such as an application running on a particular server or a server connected to specific storage or network devices.
Mapping these relationships allows IT teams to understand how one change or failure can affect other system parts. It’s beneficial during root cause analysis or risk assessment for changes.
Ongoing Maintenance
IT environments change constantly; new systems are added, old ones are retired, and configurations are updated. Continuous maintenance is required to keep the CMDB accurate.
This includes automated updates when discovery tools detect changes, periodic audits to validate data, and manual corrections where needed. Regular maintenance prevents outdated or incorrect information from undermining decision-making.
Why a CMDB Matters: Essential Benefits for Modern IT Infrastructure
Below are the essential advantages that organizations gain by implementing and maintaining a healthy CMDB.
1. Centralized Visibility Across IT Assets
A CMDB provides a single source of truth for all Configuration Items (CIs), including hardware, software, cloud services, and network components. This eliminates the data being scattered across spreadsheets, tools, or departments.
According to a Gartner study, organizations with centralized IT asset visibility reduce configuration-related outages by up to 50%.
2. Faster Incident Resolution
By linking incidents to affected CIs, the CMDB helps IT teams quickly identify the root cause of problems. This reduces mean time to resolution (MTTR) and minimizes service disruptions.
For instance, if a business-critical application goes down, the CMDB can show which server it runs on and whether any recent changes were made, speeding up troubleshooting significantly.
3. Reduced Downtime and Outages
CMDBs help prevent unplanned outages by mapping dependencies between systems. This enables proactive risk analysis before implementing any change. The Ponemon Institute reports that the average cost of IT downtime is $5,600 per minute. A well-maintained CMDB can significantly reduce this financial risk by enabling better impact analysis.
4. Improved Risk Assessment
With clear visibility into CI relationships, IT teams can anticipate the ripple effects of changes. This reduces failed changes and increases the success rate of planned maintenance.
For example, before updating a database server, the CMDB reveals that three critical applications depend on it. This insight allows for coordinated downtime planning and user notifications.
5. Enhanced Compliance and Audit Readiness
CMDBs store detailed records of CIs, including change histories and ownership. This simplifies internal and external audits by providing clear audit trails.
For organizations subject to regulations like ISO 27001 and the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) CPS 234 standard, a CMDB can demonstrate control over IT assets and configurations, supporting compliance efforts and reducing audit-related penalties.
6. Automation and Operational Efficiency
A CMDB can automatically detect and update asset data using tools like ServiceNowDiscovery, which scans your IT environment to identify hardware, software, and cloud resources in real time.
This automation eliminates the need for manual data entry, reduces errors, and ensures that the configuration data remains accurate and current. By continuously monitoring changes across the infrastructure, automated discovery provides a dynamic and reliable inventory without burdening IT teams with routine tasks.
Best Practices for Implementing CMDB in Your Organization
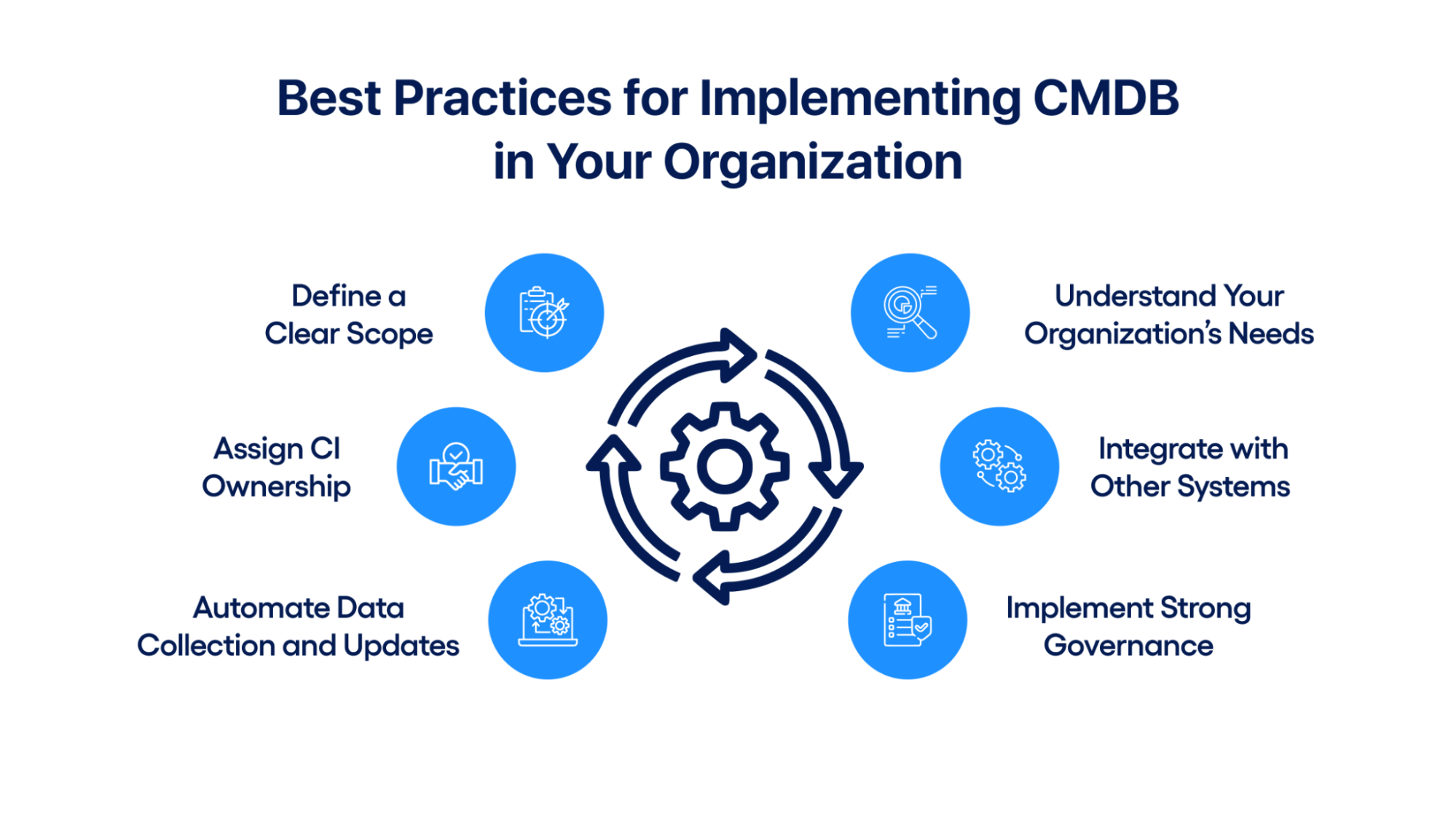
Here is a list of best practices for maintaining the CMDB as a reliable operational tool and a strategic IT Service Management (ITSM) asset.
1. Define a Clear Scope
Start by identifying what needs to be tracked in your CMDB. Not every IT component must be included; prioritize the most critical configuration items (CIs) and their relationships. Focusing on high-impact assets prevents your CMDB from becoming too complex or difficult to manage.
Before expanding to broader areas, begin with core infrastructure components like servers, applications, and network devices.
2. Understand Your Organization’s Needs
Before implementation, clearly understand what goals your CMDB is meant to support. Consider the IT services, processes, and compliance requirements that the CMDB will align with. This ensures the database is designed around real business priorities rather than theoretical models.
3. Assign CI Ownership
Every configuration item in the CMDB should have a designated owner. This person or team maintains accurate and current data for that specific CI. Clear ownership ensures accountability and supports consistent data quality.
4. Integrate with Other Systems
Your CMDB should not operate in isolation. Connect it with other systems, such as incident management, change management, asset tracking, and monitoring tools. Integration improves data accuracy and ensures that changes in one system are reflected across all relevant platforms.
For example, if a server is retired in the asset management system, that change should automatically update the CMDB.
5. Automate Data Collection and Updates
Where possible, use automated discovery tools to populate and update your CMDB. Automation minimizes human error, improves efficiency, and helps maintain a real-time view of the IT environment. Platforms like ServiceNow can scan networks and automatically register new devices or updates.
6. Implement Strong Governance
Establish governance policies to define how data is entered, maintained, and reviewed. Assign roles, responsibilities, and approval workflows. Strong governance ensures data integrity and standardization across teams. Consider focusing on data validation rules, CI lifecycle management, and access controls.
How does DKode Technologies Utilize ServiceNow CMDB to Deliver Real Results?
DKode Technologies helps organizations streamline IT asset management, improve operational visibility, and ensure compliance by utilizing the ServiceNow Configuration Management Database (CMDB) capabilities. Here is how we do it:
1. Visualizing Dependencies with Precision
Using the Dependency View, DKode Technologies lets clients visualize how different Configuration Items (CIs) are connected. This clarity supports faster root-cause analysis during incidents and ensures better impact assessments before executing changes. The result is reduced downtime and smarter decision-making during high-risk operations.
2. Automating Asset Discovery and Updates
With ServiceNow Discovery, DKode Technologies automates the detection and mapping of IT assets across networks, data centers, and cloud platforms. This ensures that the CMDB remains current, helping clients identify underutilized resources, reduce licensing costs, and maintain an accurate inventory without relying on manual updates.
3. Service-Centric Visibility
DKode Technologies uses Service Mapping to link IT infrastructure to business services. This allows organizations to understand how specific components support key operations. When issues arise, teams can quickly assess which services are affected and respond proactively—minimizing impact and improving service reliability.
4. Secure Integration with On-Premises Systems
DKode Technologies ensures secure communication between ServiceNow and on-premises infrastructure through the MID Server. This enables seamless data collection and integration, helping clients consolidate systems without exposing sensitive environments to risk.
5. Smarter Event Management
DKode Technologies implements AI-driven Event Management to reduce alert fatigue and focus teams on high-priority incidents. By correlating and filtering events in real time, clients can reduce noise, detect issues faster, and improve response times—leading to more stable and reliable IT operations.
6. Workflow Automation for Greater Efficiency
Using Orchestration, DKode Technologies automates routine processes like password resets, server provisioning, and software installations. This improves service delivery speed, reduces human errors, and frees up teams for higher-value work.
Streamline IT Asset Management With DKode’s ServiceNow CMDB Solutions

At DKode Technologies, we help organizations structure, scale, and streamline service delivery using the ServiceNow platform. But our work extends beyond support; we connect internal workflows with external demands to deliver measurable outcomes across teams.
Our certified ServiceNow professionals and ITIL Practitioners bring deep industry expertise and a proven ability to solve complex challenges. What sets us apart is our technical expertise and a strong, collaborative team culture built on trust, shared learning, and a commitment to excellence.
We support organizations across multiple service areas:
- Enterprise IT Solutions – End-to-end IT services including ITSM, ITAM, CMDB, and Security Operations tailored for enterprise efficiency and resilience.
- Software Development Solutions – Custom software solutions built to meet unique business needs with speed, flexibility, and scalability.
- Managed Support Services – Reliable, ongoing technical support to maintain system stability and ensure optimal performance
- Customer and Industry Solutions – Tailored ServiceNow CSM solutions to enhance customer experiences
- Asset Management – that offers complete visibility into hardware, software, and services—enabling accurate tracking, better control, and more efficient planning.
- IT Operations Management (ITOM) – to monitor systems, prevent disruptions, and ensure consistent performance across environments
By combining ITSM, CSM, and ITOM, we help businesses move faster, work smarter, and scale confidently, backed by a team as invested in your success.
Contact Us